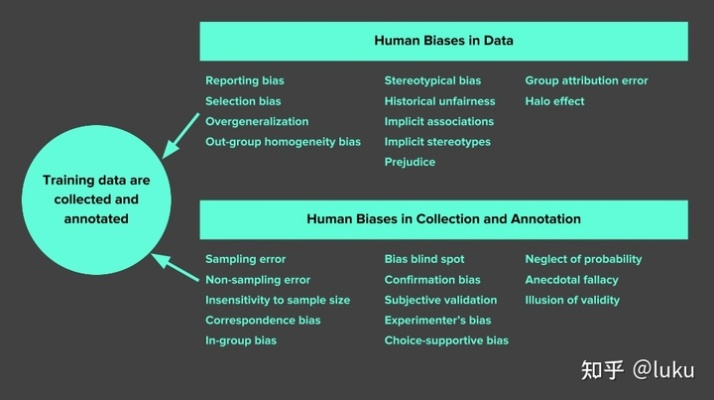
直接参与英语翻译
Title: Effective Strategies for Translating English
Introduction:
English translation involves converting text or speech from English to another language while preserving the meaning, style, and tone of the original content. It requires strong language skills, cultural understanding, and knowledge of various industries. In this article, we will explore effective strategies for translating English and provide guidance for achieving accurate and fluent translations.
1. Contextual Understanding:
One of the key aspects of successful translation is grasping the context of the source material. Translators should thoroughly analyze the text, including its purpose, target audience, and cultural nuances. By understanding the context, translators can ensure that the translated content effectively conveys the intended message and resonates with the target audience.
2. Vocabulary Research:
Translators must possess a vast vocabulary in both the source and target languages. When encountering unfamiliar terms or phrases, conducting thorough research is essential. Online dictionaries, glossaries, and participation in professional forums can provide valuable resources for expanding vocabulary and finding the most appropriate translations for specific industries or subjects.
3. Adapting to Cultural Differences:
Languages are deeply intertwined with their cultures. Effective English translation requires adjusting the content to fit the cultural context of the target language. Translators must be sensitive to cultural differences, social norms, and idiomatic expressions to ensure that the translated text is culturally appropriate and relevant. Adapting the tone and style of the original content can significantly enhance the quality of the translation.
4. Utilizing Translation Tools:
Advancements in technology have brought numerous translation tools and software that can facilitate the translation process. Translators can use Translation Memory (TM) software to store and retrieve previously translated phrases, reducing repetitive work and ensuring consistency in terminology. Machine translation tools can also be used to generate initial translations, which can then be refined by human translators for accuracy and fluency. However, it is important to note that these tools are aids and not substitutes for human translators.
5. Collaboration and Proofreading:
Translation is a collaborative process, especially for extensive or complex projects. Translators can seek support and feedback from colleagues or subject matter experts to enhance the overall quality of the translation. Additionally, thorough proofreading is crucial to eliminate errors, improve language fluency, and ensure consistency. Collaborative efforts and thorough proofreading contribute to delivering accurate and polished translations.
6. Continuous Professional Development:
Language is an everevolving entity, and translators must stay updated with changes in vocabulary, grammar, and linguistic trends. Engaging in continuous professional development, attending language workshops, and actively participating in translation communities can help translators improve their skills and stay at the forefront of industry trends.
Conclusion:
Translating English accurately and proficiently requires a combination of linguistic skills, cultural understanding, and effective utilization of translation tools. By adopting strategies such as contextual understanding, vocabulary research, adapting to cultural differences, utilizing translation tools, collaborating with peers, and investing in continuous professional development, translators can deliver highquality translations that effectively communicate the original message.