Understanding and Improving ChineseStyle English Translation
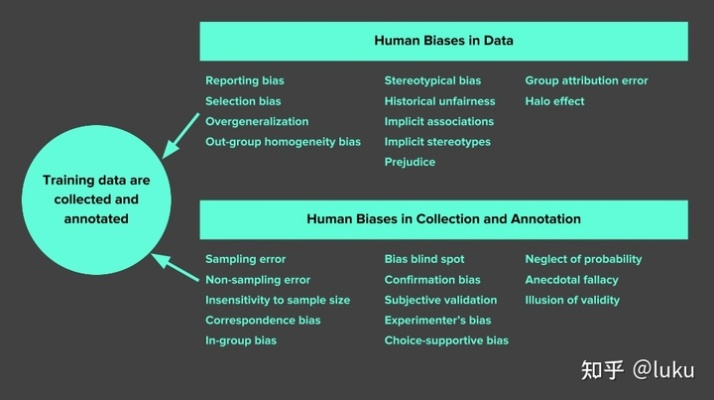
In recent years, Chinesestyle English translation has garnered increased attention due to its unique characteristics and challenges. This form of translation, also known as "Chinglish," often involves direct translations of Chinese phrases or idioms into English, resulting in awkward or confusing language. To better understand and improve Chinesestyle English translation, it is essential to delve into the key considerations and strategies that can enhance the quality and accuracy of the translated text.
1. Cultural Differences:
One of the primary challenges in Chinesestyle English translation lies in navigating the cultural nuances embedded within the language. As Chinese and English are rooted in vastly different cultural contexts, direct translations without considering cultural differences can lead to misinterpretations or inaccuracies.
2. Idiomatic Expressions:
Chinese language is rich in idiomatic expressions that may not have direct equivalents in English. Translating these expressions wordforword can result in nonsensical or humorous outcomes. It is crucial for translators to interpret the intended meaning behind the Chinese idioms and convey it effectively in English.
3. Syntax and Grammar:
Chinese syntax and grammar differ significantly from English, posing a challenge for translators to maintain coherence and readability in the translated text. Adhering to English language rules while capturing the essence of the original Chinese text is a delicate balancing act that requires careful attention to detail.
1. Transcreation:
Instead of adhering strictly to literal translations, transcreation involves capturing the original intent and emotions of the text and expressing them in a culturally appropriate manner in English. This approach allows for greater flexibility and creativity in conveying the essence of the Chinese text.
2. Localization:
Localization involves adapting the translated text to suit the linguistic and cultural norms of the target audience. By customizing the translation to resonate with Englishspeaking readers, localization ensures that the message is effectively communicated without losing its original meaning.
3. Collaborative Translation:
Collaborative translation brings together bilingual experts and native speakers of English to work collectively on translating Chinese text. This collaborative effort helps in crosschecking for accuracy, cultural relevance, and linguistic nuances, leading to a more polished and refined translation.
Improving Chinesestyle English translation requires a nuanced understanding of both languages, as well as the cultural contexts in which they are embedded. By emphasizing cultural sensitivity, linguistic accuracy, and creative adaptation, translators can overcome the challenges associated with Chinesestyle translation and deliver highquality, readerfriendly content in English.